
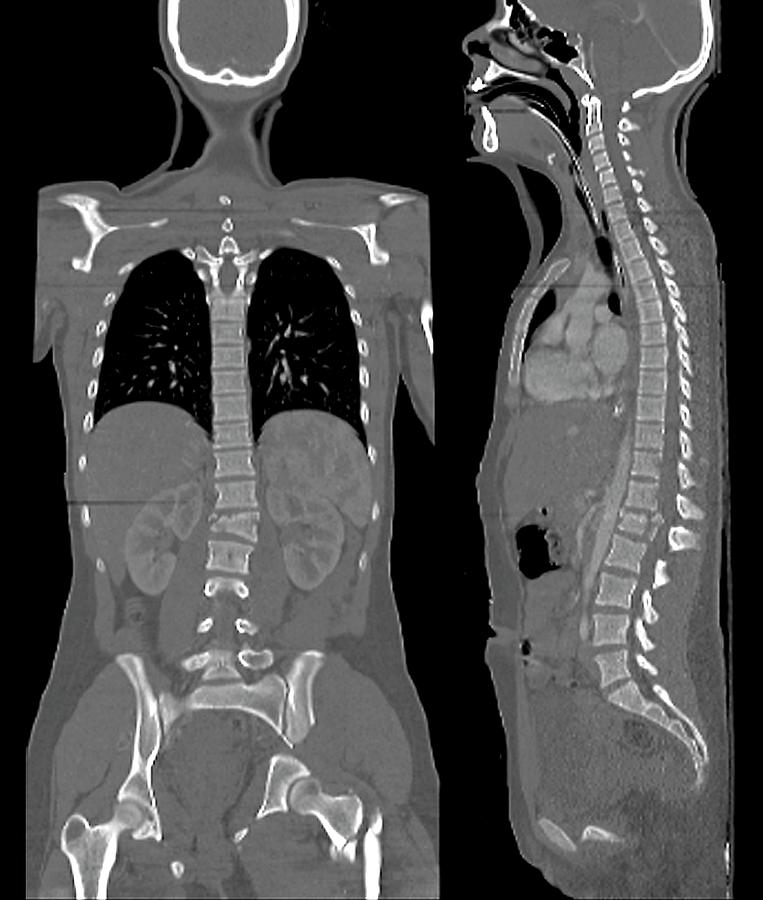
based on pelvic stability and useful for guiding pelvic reconstruction.Hip fractures occur to the top portion of the femur and per se, are not considered a pelvis fracture, thus are not included in this discussion.There are various systems for classification, these are the 2 most often used: Lateral crush injury: Like the other two fractures, half of the pelvis is crushed either inward or outward, again, resulting in damage to surrounding vessels and structures. Like an open book, tears in the pelvic ligaments, as well as in the sacral ligaments can result in massive blood loss. Vertical shear pelvis injury: This is when one half of the pelvis shifts upwards.

This requires an emergency intervention to stop the blood loss. Also, pelvis veins can bleed in this location. Large arteries pass near these ligaments and can get torn resulting in massive blood loss. This injury results in tears of the strong pelvic ligaments that hold the pelvis bones together. Open-book pelvis injury: In this instance, the front of the pelvis opens like a book. These injuries are considered life-threatening due to the potential for damage to surrounding blood vessels and nerves. Surgery in this area, in part, depends on the status of the remainder of the pelvis bones. Fractures through the sacrum, or injury that produces a widening where the iliac wings attach may result in an “unstable” pelvis – that is, surgical intervention may be required to allow for appropriate healing. The iliac wings of the pelvis attach to the sacrum, the lowest portion of the spine. Iliac Wing:įractures of the iliac wing, while painful, generally do not require surgery. Of importance, the blood supply to the “ball joint” of the femur is in this location, so early “relocation” is important. If there are no associated fractures, further surgery is usually not warranted. Manipulation in the emergency department or the operating room allows for “relocation” of the joint. Breaks in this area, depending upon location and severity, may require surgery to stabilize the joint. The integrity of this socket is what keeps the ball of the femur in place. Acetabulum:Īcetabulum fractures, or fracture of the “socket” of the hip are more problematic. Often, a walker is used for stability, until pain has diminished. Usually, within 24-48 hours, patients are encouraged to be up and walking. Fractures in these locations, while painful, generally do not require surgery. The two sets of rami are essentially two rings attached in the middle at the pubis symphysis. This is the bottom-most portion of the pelvis and comprises the bones we sit on. Also, certain types of pelvis injury are life-threatening and need urgent attention. The pelvis is divided into several sections, and the need for surgery depends upon which section is injured. Knowing this, when one fracture is seen, careful inspection is undertaken to look for a second fracture. The pelvis is like a pretzel, it is impossible to break the pelvis in one location without suffering a break (fracture) in a second location. The anatomy of the pelvis is diagrammed below: Fortunately, a majority of pelvis fractures are minor, and while painful, do not require any surgery. Injury to the pelvis occurs in approximately 8-9% percent of what is termed blunt trauma: falls, motor vehicle crashes (cars and motorcycles), bicycle wrecks, and pedestrians being struck by moving vehicles. Critical Care Committee Journal Reviews.Past Research and Education Scholarship Recipients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
